

BLOOD BUMP ON VAGINA SKIN
age – vulvar cancer usually occurs in postmenopausal women, but there appears to be an increasing number of young women being diagnosed.

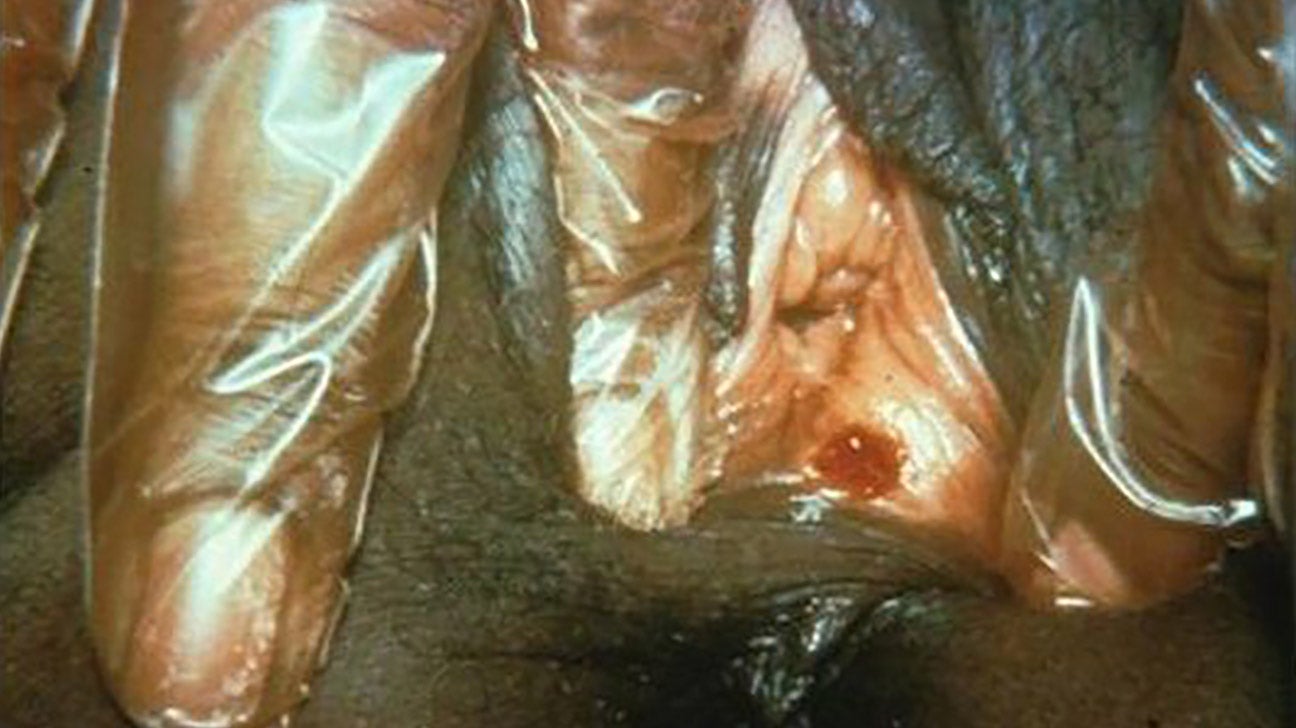
Some of the risk factors for vulvar cancer include: In advanced cases secondary cancers may cause a range of symptoms, such as fatigue, loss of weight, aching bones.Problems with bowel motions and passing urine may indicate the cancer has spread into the bowel or bladder.The lymph glands in the groin may swell.There could be unusual bleeding or discharge from the vagina.The raw-looking sore can be white, red or pink.The lump progresses to an ulcerated sore that refuses to heal.An unusual lump or bump can be felt somewhere on the vulva.In its early stages, vulvar cancer often has no symptoms. Without treatment, it can cause severe infection and pain. As the cancer grows it usually spreads to nearby body parts such as the bladder, vagina and anus. The most common site for vulvar cancer is the labia majora, while just one in 10 cases affect the clitoris. However, an increasing number of women aged 35 to 45 are being diagnosed with this form of cancer. It accounts for about three per cent of all gynaecological cancers and is most commonly diagnosed in older women aged around 70 years or over. Vulvar cancer is a type of cancer that affects the vulvar region. The vulva is made up of three main parts: the labia majora (outer lips), the labia minora (smaller inner lips) and the clitoris. Vulva is a general term that describes the external female genitals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
